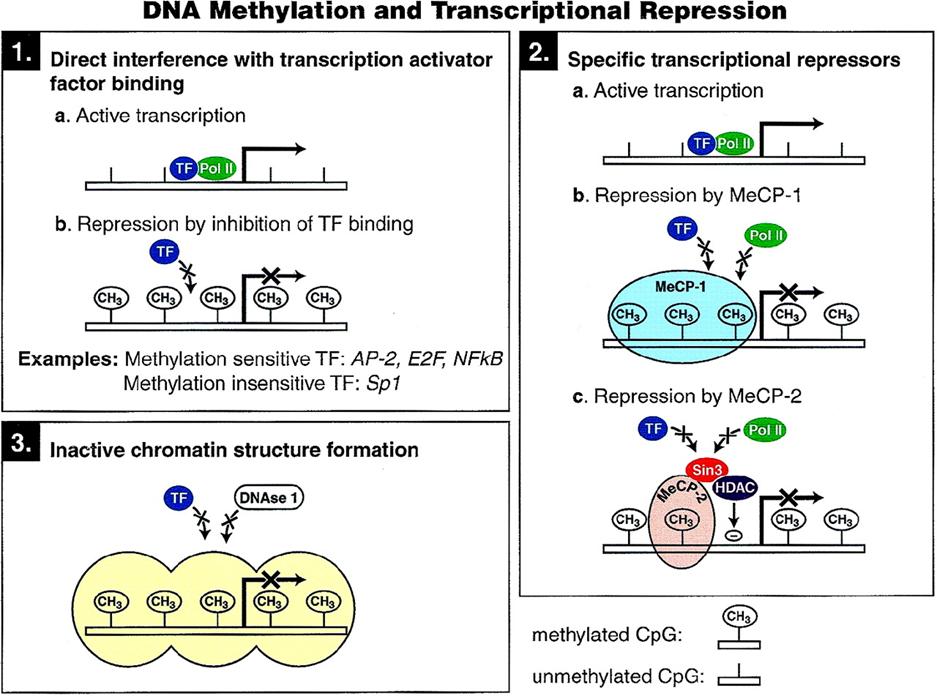
Hiszton módosítás
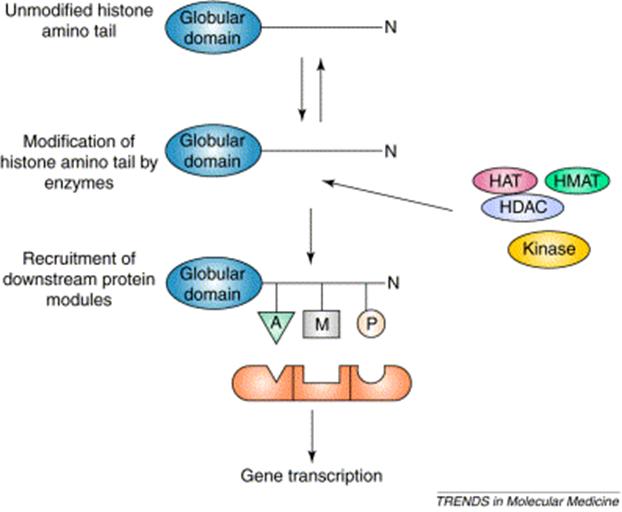
hiszton
amino-terminális domainek kovalens módosításai:
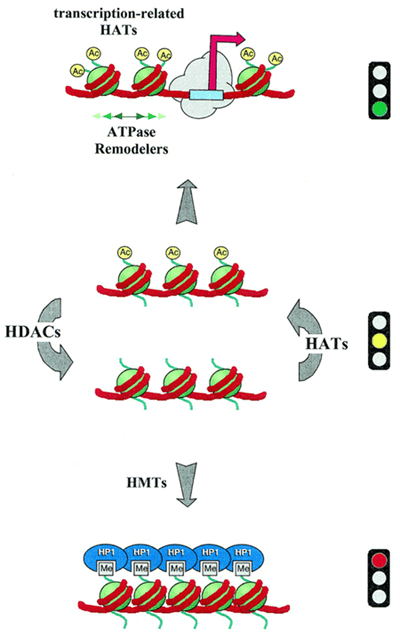
acetiláció (A) az acetilációs egyensúlyt a hiszton
acetil-transzfrázok (HAT) és hiszton deacetilázok (HDAC) biztosítják (lys)
metiláció (M) a hiszton
metil-transzferázok (HMAT) végzik
foszforiláció (P) kinázok
további módosítások: ubiquitináció
és ADP-riboziláció
a módosítások feltehetően a génátírást szabályozó
fehérjék kötéséhez járulnak hozzá
transzkripció – kromatin
szerkezet - hisztonok
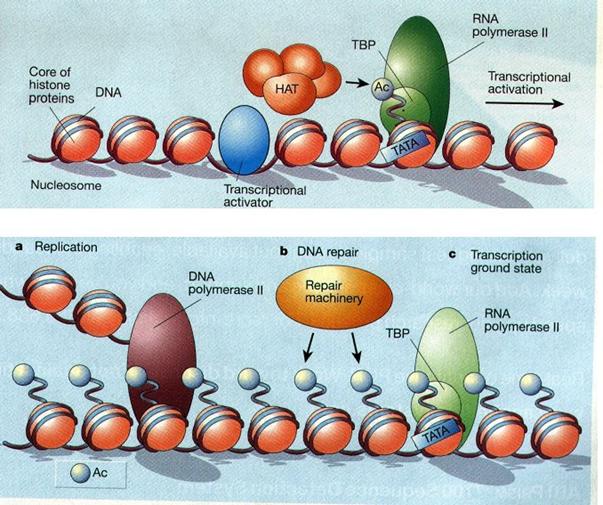
HAT molekulacsaládok és transzkripciós szerepük
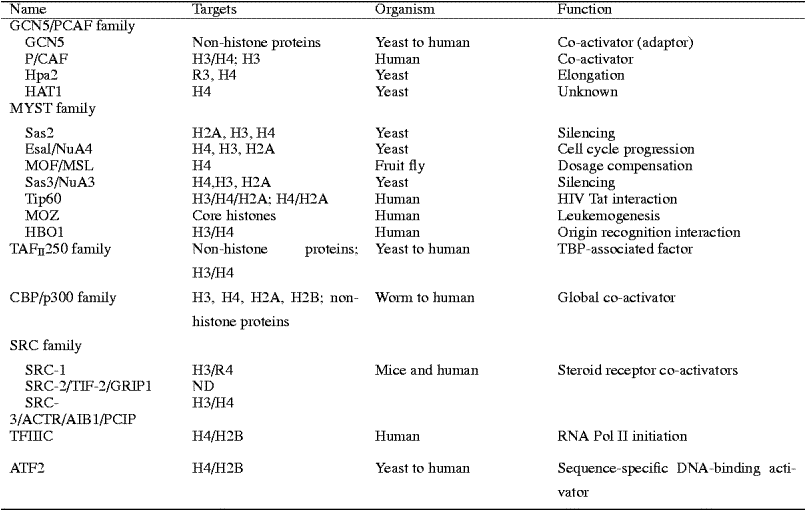
Summary of HATs and their native complexes.
The HATs are shown as families based on
distinguishable structural homology.
The transcription related functions and histone
specificity are shown
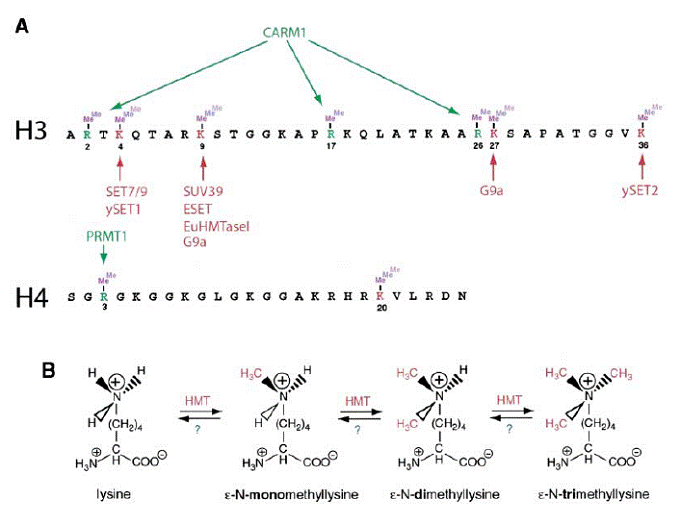
hiszton
metiláció
Lys
(K) és Arg (R)
|
|
a
hiszton-módosítások szerepe
|
a hiszton metiláció biológiai szerepe
|
|
példa:
ciklin E promóter
|
G1 fázis inaktív H3K9 metiláció |
S fázis aktív H3K9 demetiláció |
hiszton
metiláció közvetítésével 'kikapcsolt' génműködés
|
|
|
|
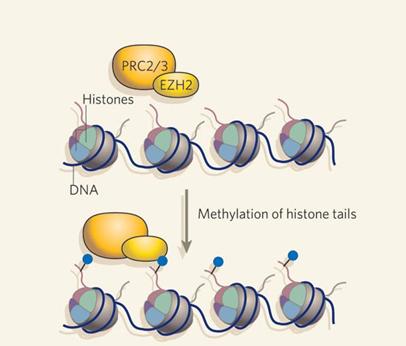
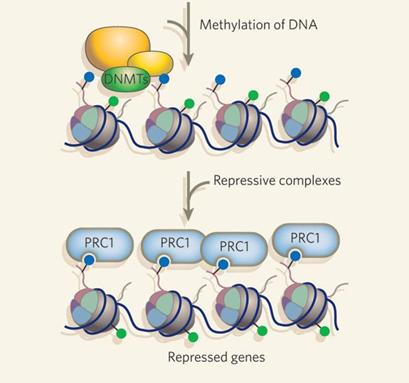
EZH2: histone-lysine methyltransferase,
működése a PRC 2/3-kötéstől függ
PRC2/3 (Polycomb Repressive Complexes 2 és 3): mennyiségük
daganatsejtekben emelkedett
PRC1: represszor, a zárt kromoszóma-szerkezet fenntarásáért
tehető felelőssé
|
|
HP1 (heterochromatin-associated protein-1):
'felismeri' a 'hiszton kódot' azaz a metilált Lys9
(methyl-K9) a H3 hisztonon
|
|
érdekes
Genes Dev. 2010 Oct 1;24(19):2133-45.
Heterochromatin
protein 1 (HP1) connects the FACT histone chaperone complex to the
phosphorylated CTD of RNA polymerase II.
Kwon SH, Florens L, Swanson SK, Washburn MP, Abmayr SM, Workman JL.
Heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) is well known as a silencing protein
found at pericentric heterochromatin. Most eukaryotes have at least three
isoforms of HP1 that play differential roles in heterochromatin and
euchromatin. In addition to its role in heterochromatin, HP1 proteins have been
shown to function in transcription elongation. To gain insights into the
transcription functions of HP1, we sought to identify novel HP1-interacting
proteins. Biochemical and proteomic approaches revealed that HP1 interacts with
the histone chaperone complex FACT (facilitates chromatin transcription). HP1c
interacts with the SSRP1 (structure-specific recognition protein 1) subunit and
the intact FACT complex. Moreover, HP1c guides the recruitment of FACT to
active genes and links FACT to active forms of RNA polymerase II. The absence
of HP1c partially impairs the recruitment of FACT into heat-shock loci and
causes a defect in heat-shock gene expression. Thus, HP1c functions to recruit
the FACT complex to RNA polymerase II.
érdekes
JBC,
Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 38090-38095.2005
HP1 Binds Specifically to Lys26-methylated
Histone H1.4, whereas Simultaneous Ser27 Phosphorylation Blocks HP1
Binding*
1. Sylvain
Daujat‡,1,
2. Ulrike
Zeissler‡,1,
3. Tanja
Waldmann‡,
4. Nicole
Happel§
and