NF-kB
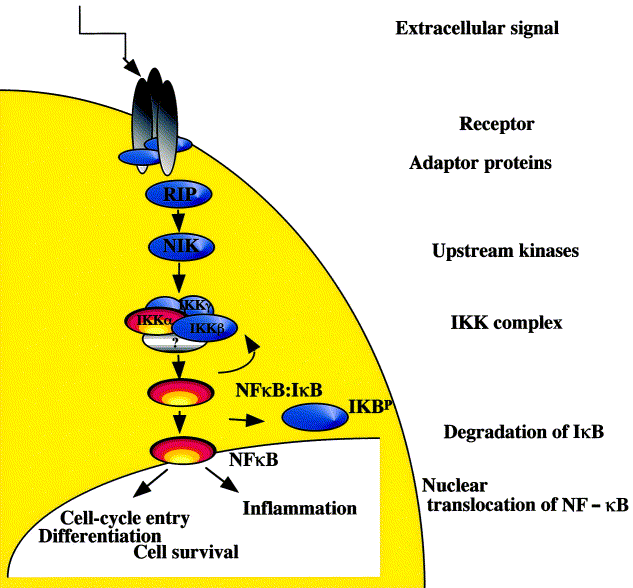
Fig. 1. Regulation of NF-![]() B activity. Extracellular signals lead to activation of the IKK
complex through proteins referred to as adaptors. (The IKK kinase complex is the core element of
the NF-κB cascade. It is essentially made of two kinases (IKKα and
IKKβ) and a regulatory subunit, NEMO
B activity. Extracellular signals lead to activation of the IKK
complex through proteins referred to as adaptors. (The IKK kinase complex is the core element of
the NF-κB cascade. It is essentially made of two kinases (IKKα and
IKKβ) and a regulatory subunit, NEMO![]() , IK
, IK![]() ), a structural regulatory subunit (IKK
), a structural regulatory subunit (IKK![]() or NEMO) and several other associated
proteins. Induction of the IKK complex phosphorylates the I
or NEMO) and several other associated
proteins. Induction of the IKK complex phosphorylates the I![]() B proteins (I
B proteins (I![]() B
B![]() , I
, I![]() B
B![]() and I
and I![]() B
B![]() ) which are then ubiquitinated and
degraded. NF-
) which are then ubiquitinated and
degraded. NF-![]() B is released and translocates to the nucleus interacting with target
DNA sequences, other transcription factors and co-activator proteins that
regulate histone acetylase activity. The figure depicts the recently described
pathway of TNF–receptor signaling through the adaptor protein RIP and the
upstream kinase NIK.
B is released and translocates to the nucleus interacting with target
DNA sequences, other transcription factors and co-activator proteins that
regulate histone acetylase activity. The figure depicts the recently described
pathway of TNF–receptor signaling through the adaptor protein RIP and the
upstream kinase NIK.
Target Genes of NF-kB
Cytokines/Chemokines and their Modulators
Immunoreceptors
Proteins Involved in Antigen Presentation
Cell Adhesion Molecules
Acute Phase Proteins
Stress Response Genes
Cell Surface Receptors
Regulators of Apoptosis
Growth Factors, Ligands
and their Modulators
Early Response Genes
Transcription Factors and Regulators
Viruses
Enzymes
Miscellaneous