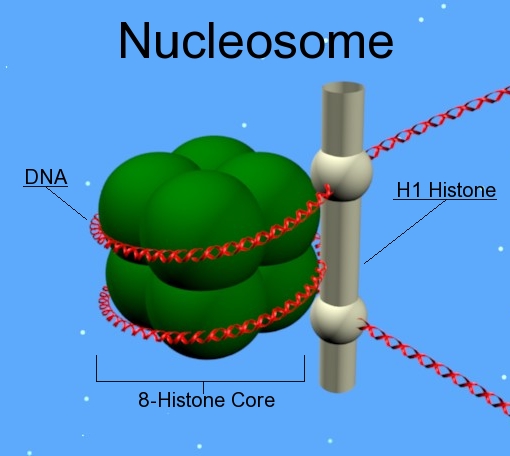
kromatin struktúra: nukleoszóma
8
hiszton molekula (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4)
146
bp DNS
|
|
szerkezetváltozás
– ’remodeling’
(pl. osztódásnál relaxált v.
kondenzált, génátírásnál)
ATP
függő
SWI–SNF és
NURF complexek
SWI/SNF
family of complexes utilizes the energy of ATP hydrolysis to remodel chromatin
structures. The nucleosome remodeling factor (NURF) is one of several
ISWI-containing protein complexes that catalyze ATP-dependent nucleosome
sliding and facilitate transcription of chromatin in vitro. NURF is required
for transcription activation in vivo.
hiszton módosító fehérjék
foszforiláció, poli-ADP-riboziláció, metiláció,
acetiláció, ubiquitináció
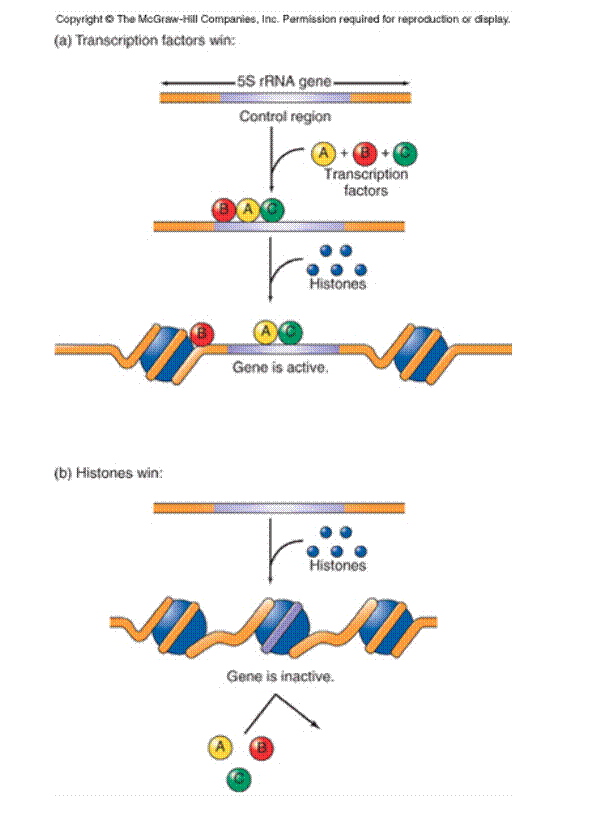
nukleoszóma
szerkezet-változtatások – génexpresszió
(hisztonok és transzkripciós
faktorok ’harca’)
|
|
Hogyan
változtatják a génexpressziót a hisztonok poszt-transzlációs módosításai?
Lys – módosítása (ac)
HAT(1-8) – hiszton acetil-transzferázok
Histone acetylation involves the
transfer of an acetyl group from acetyl Co-A to the ![]() -amino group of lysine side chains within the
substrate, Acetylation of target substrates regulates protein function. In the
case of transcription factors, acetylation may alter DNA binding,
protein–protein interaction or subcellular localization. Acetylation plays a
key role in coordinating sequential post-translational modifications of
substrates by phosphorylation, methylation and other modifications such as
ubiquitination. The removal of the acetyl groups from lysine residues from
these substrates is conducted by histone deacetylases (HDACs 1–8). Distinct
signal transduction processes regulate the abundance, subcellular distribution
and activity of HDACs. Ref: Acetylation
in hormone signaling and the cell cycle. Maofu
Fu, Chenguang Wang, Jian Wang, Brian T. Zafonte, Michael P. Lisanti and Richard
G. Pestell, Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews, Vol.13 (3), June 2002,
pp259-276
-amino group of lysine side chains within the
substrate, Acetylation of target substrates regulates protein function. In the
case of transcription factors, acetylation may alter DNA binding,
protein–protein interaction or subcellular localization. Acetylation plays a
key role in coordinating sequential post-translational modifications of
substrates by phosphorylation, methylation and other modifications such as
ubiquitination. The removal of the acetyl groups from lysine residues from
these substrates is conducted by histone deacetylases (HDACs 1–8). Distinct
signal transduction processes regulate the abundance, subcellular distribution
and activity of HDACs. Ref: Acetylation
in hormone signaling and the cell cycle. Maofu
Fu, Chenguang Wang, Jian Wang, Brian T. Zafonte, Michael P. Lisanti and Richard
G. Pestell, Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews, Vol.13 (3), June 2002,
pp259-276
H3 N-terminális foszforilálása – fellazítja a
hiszton-DNS kötést, jobban hozzáférnek a transzkripciós faktorok a DNS-hez
a módosítások
felismerőhelyeket hozhatnak létre: TAFII250-nek intrinsic HAT
aktivitása van, ac-Lys-hez kötődik
Activation of RNA-polymerase-II-dependent transcription
involves conversion of signals provided by gene-specific activator proteins
into the synthesis of messenger RNA. This conversion requires dynamic
structural changes in chromatin and assembly of general transcription factors
(GTFs) and RNA polymerase II at core promoter sequence elements surrounding the
transcription start site of genes. One hallmark of transcriptional activation
is the interaction of DNA-bound activators with coactivators such as the
TATA-box binding protein (TBP)-associated factors (TAF(II)s) within the GTF
TFIID.
acetiláció megnöveli a
hiszton-karok ![]() -helix
tartalmát
-helix
tartalmát
traszkripció-aktivátorok
HAT-okat ’toboroznak’ a promóterekhez a szerkezetváltozát követően
EREDMÉNY:
az
acetiláció-függő módosítások destabilizálják a promóter régiók nukleoszóma
szerkezetét, elősegítik a transzkripciós faktorok DNS-felismerését/kötését